
However, the reason that Gauss’s Law is so powerful is because we exploit symmetry within our system. A surface (which we define with an area vector or.
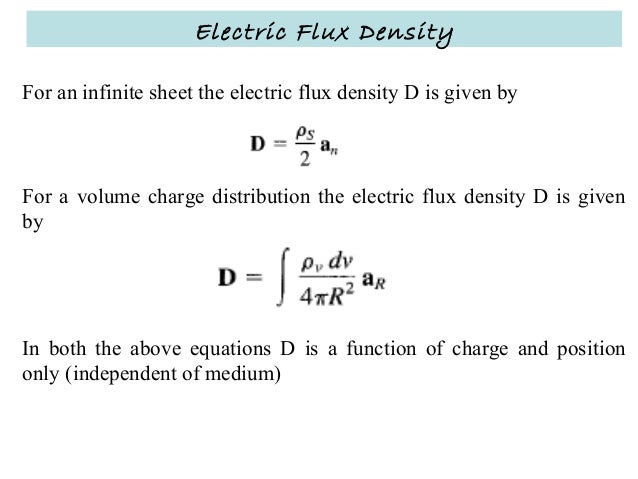
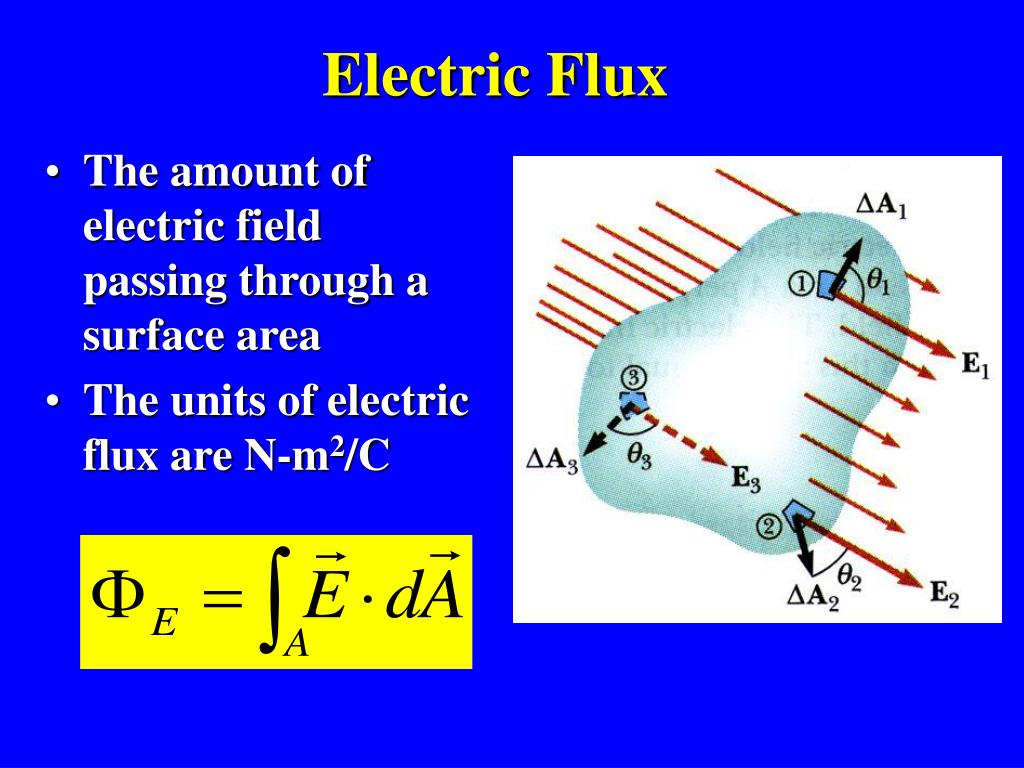
If we couple Gauss’s law with the remaining three Maxwell’s equations, we can solve for the propagation of light within a material. In order to calculate an electric flux, you need two things: 1. When we express the electric field of a system in terms of voltage, we can use it to derive Poisson’s equation or Laplace’s equation. We can use it to determine all sorts of properties of electric fields in media. You generally see them in a more advanced course on electricity and magnetism. There are, of course, many other symmetries out there. Where each \(A\) gives the area of the top, bottom, and side of the cylindrical Gaussian surface. The differential form of the equation states that the divergence or outward flow of electric flux from a point is equal to the volume charge density at that point. The electric flux is simply the amount of electric field passing through a surface. The above integral equation states that the electric flux through a closed surface area is equal to the total charge enclosed. An Overview of Electric Flux and Gauss’s Law Specifically, I want to look at the difference between the total flux over the entire surface and the flux at each individual point on the surface. I want to focus on one specific part of Gauss’s law this week: the electric flux on the Gaussian surface. It is probably the first time that they are given a real-world example of when we actually use the abstract concept of a vector field over a closed surface. After teaching Gauss’s law for a number of years (as well as thinking back to when I was learning it), I know that it can be pretty difficult for students to grasp the nuances of what is actually going on.
The Gauss law calculator gives you the value of the electric flux in the field "Electric flux ϕ": In this case, ϕ = 1129 Vm.This past week we covered Gauss’s law in my introductory physics classes.Enter the value 10 nC in the field "Electric charge Q".You can do so using our Gauss law calculator with two very simple steps: 0o (the angle between the electric field direction and a line drawn a perpendicular to the area) electric flux (Nm2/C), E electric field (N/C), A area (m2), q angle between. Also read - NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics NCERT Solutions for Class 12. A uniform electric field E 8000 N/C passing through a flat square area A 10 m2. is the angle between the electric field lines and normal to A. You can however select a different unit for the electric charge.įor example, let's say you want to calculate the magnitude of the electric flux through a closed surface around a 10 nC electric charge. Uniform Electric Field: The formula of Electric Flux: The Electric Flux passing through the surface of vector area A is.
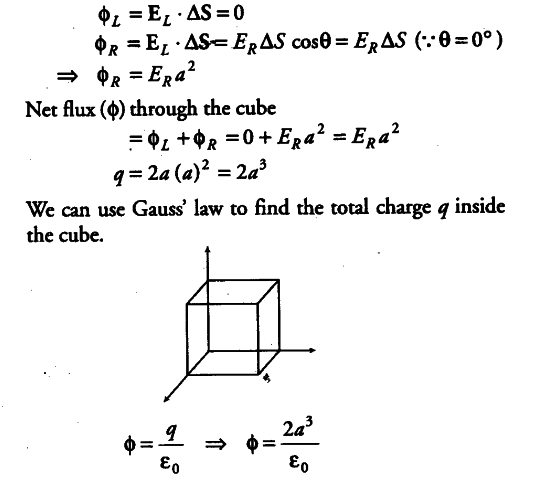
The unit of electric charge is set by default to nC (nanocoulomb) to get flux and charge numbers of similar orders of magnitude. The unit of electric flux used in this calculator is Vm or, equivalently, Nm 2/C. Remember, it is constant and shouldn't be changed except in certain special cases. You can also click on Advanced mode to see the exact value of the vacuum permittivity ε 0. When using the Gauss's law calculator, you can either input the value of the electric charge Q to receive the electric flux ϕ, or you can provide the electric flux ϕ and the calculator will give you the corresponding electric charge Q.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
